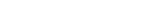Key Takeaways
- L-Carnitine is a naturally occurring nutrient involved in energy metabolism.
- It helps transport fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production.
- May provide benefits in exercise performance, recovery, and fat metabolism.
- Generally well-tolerated but may cause mild side effects in some individuals.
- Widely researched in both humans and animals for metabolic functions.
Quick Facts
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Category/Class | Amino acid derivative |
| Research Status | Extensive human/animal research |
| Typical Effects | May enhance fat metabolism, energy |
| Known Risks | Mild GI upset, rare odor disturbance |
| Legal Status | Legal, OTC supplement in most regions |
What Is L-Carnitine?
L-Carnitine is an amino acid derivative produced in the body and found in many foods, especially red meat.
- It plays a key role in transporting long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria for energy production.
- Studied for its effects on metabolism, exercise performance, and certain medical conditions such as heart disease.
- It is classified as a nutrient and often used as a dietary supplement.
How L-Carnitine Works
Mechanism of Action
- L-Carnitine shuttles fatty acids from the cytosol into mitochondria of cells.
- Inside mitochondria, fatty acids are burned to produce ATP (energy).
- Supports cellular energy production, especially during exercise or stress.
- Enhances removal of toxic compounds from mitochondria.
Biological Effects / Intended Actions
- Increases energy availability in cells.
- May enhance exercise performance and recovery.
- Supports fatty acid metabolism and weight management.
- Possible neuroprotective and cardioprotective roles.
Benefits of L-Carnitine
Muscle / Strength / Performance
- Improves post-exercise recovery and reduces muscle soreness.
- May enhance endurance performance in some populations.
- Potentially increases oxygen supply to muscles during exercise.
Fat Loss / Body Composition
- Promotes the breakdown of fat for use as energy.
- Some studies suggest modest support for weight or fat loss.
Other Potential Effects
- May support heart health and reduce symptoms in certain heart conditions.
- Potential neuroprotective effects in aging or neurodegenerative diseases.
- Supportive in some fertility cases for men.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Supports energy metabolism and fat loss | Mild gastrointestinal upset |
| May enhance muscle recovery after exercise | Fishy body odor (rare) |
| Possible benefits for heart and neurological health | Conflicting evidence for weight loss |
| Well-studied with robust safety profile | Not a magic bullet for performance |
Side Effects & Safety
Short-Term Side Effects
- Mild nausea, stomach upset, diarrhea are most common (NIH Fact Sheet).
- Possible “fishy” body odor (rare).
- Headache or agitation in rare cases.
Long-Term / Unknown Risks
- Long-term supplementation considered safe in moderate doses for most.
- High doses may slightly increase TMAO (linked to cardiovascular risk).
- Safety in pregnancy, children, or those with severe kidney issues is less certain.
Interactions & Special Considerations
- Can interact with some thyroid and anticoagulant medications.
- Special caution in individuals with kidney disease due to metabolite buildup.
- Always consult a physician before combining with other supplements or drugs.
How Researchers Use L-Carnitine
Research Context / Study Setups
| Study | Model | Dose/Setup | Main Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral L-carnitine in heart failure patients | Human | 2 g/day for 12 weeks | Improved cardiac function [PMID:9553568] |
| L-carnitine for muscle recovery after exercise | Human | 2 g/day for 3 weeks | Less muscle damage, soreness [PMID:18175936] |
| L-carnitine in obesity/fat loss | Human | 1-3 g/day for 8-12 weeks | Modest fat loss, mixed results [PMID:21561429] |
| Neuroprotection in rat stroke model | Animal | 100 mg/kg IV, single dose | Reduced brain injury, improved recovery |
Comparison to Similar Compounds
| Compound | Primary Use | Mechanism | Strength/Effect Size | Known Risks | Regulatory Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetyl-L-Carnitine | Cognitive, nerve health | Similar transport role, crosses BBB | Neuroprotective moderate | GI upset, rare agitation | Legal OTC |
| Creatine | Muscle performance, energy | ATP buffering/recycling | Strong for strength | GI upset, rare muscle cramp | Legal OTC |
| CLA | Fat loss | Alters fat metabolism | Mild, inconsistent | GI upset, insulin issues | Legal OTC |
| Beta-Alanine | Muscle endurance | Buffers muscle pH (carnosine) | Moderate for exercise | Tingling at high doses | Legal OTC |
| Carnitine Tartrate | Performance, recovery | Same as L-carnitine | Similar to L-carnitine | As above | Legal OTC |

Legality & Regulatory Status
- Legal as a nutritional supplement in the United States, European Union, Canada, and most regions.
- Not banned by WADA (World Anti-Doping Agency).
- Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA.
- Available without prescription for dietary use.
Where to Buy / Availability (Research-Use Only)
- L-Carnitine is widely available as a supplement for research or dietary purposes.
- Forms include capsules, tablets, and powders.
- Not approved as a drug for treatment outside certain prescription uses (e.g., primary carnitine deficiency).
- Always ensure sourcing from reputable, lab-tested suppliers—avoid unregulated online sources.
Alternatives
Recommended Alternatives
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR) — for cognitive/neuroprotective research.
- Creatine monohydrate — strong evidence for muscle strength/performance.
- Beta-Alanine — safe, well-researched for endurance.
- Balanced diet and aerobic exercise — proven methods for fat loss, metabolic health.

FAQ
1. What exactly does L-Carnitine do in the body?
L-Carnitine helps transport fatty acids into mitochondria where they are burned for energy. It plays a crucial role in fat metabolism and cellular energy.
2. Are there proven benefits for weight loss?
Evidence is mixed; some studies suggest modest effects, but it is not a guaranteed fat loss aid.
3. Is L-Carnitine safe to take every day?
Generally safe at recommended doses for most healthy adults, but consult your doctor if you have health conditions.
4. Can athletes use L-Carnitine legally?
Yes, it is not banned by sporting authorities like WADA.
5. What are the common side effects?
Mild stomach upset, diarrhea, and rare body odor changes are most reported.
6. Does L-Carnitine help with heart health?
Some evidence supports benefits in specific heart conditions (e.g., heart failure), but not as a primary treatment for all.
7. Is supplementation necessary?
Most people produce enough; supplements may be helpful in deficiency, strict vegans, or certain clinical situations.
Conclusion
L-Carnitine is an amino acid derivative vital for transporting fatty acids into mitochondria, supporting energy production and metabolism. It is researched for potential benefits in exercise recovery, fat metabolism, and certain health conditions such as heart disease and neurological disorders. While generally safe and well-tolerated, mild side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort may occur, and some risks exist for high-dose or long-term use, especially in specific populations.
Legally available and not banned in sports, L-Carnitine can be found as a supplement in most regions—though not all claims are strongly supported by science. If considering alternatives, options like Acetyl-L-Carnitine or creatine offer robust evidence for performance. For most individuals, a healthy lifestyle remains the foundation for metabolic health and energy.