Introduction
Fenugreek is a popular herbal supplement valued in athletic and bodybuilding circles for its potential impact on muscle strength, recovery, metabolism, and hormone regulation.
Despite its widespread use, many athletes remain unclear about how Fenugreek actually works, what the evidence shows, and how to use it safely and effectively.
This comprehensive, evidence-based guide explores Fenugreek’s mechanisms, benefits, risks, usage, and practical considerations tailored for performance-focused individuals, without hype or unfounded claims.
Key Takeaways
- Fenugreek is an herbal supplement commonly used to support metabolic health, muscle recovery, and hormonal balance.
- Human research suggests potential benefits, but results can be context-dependent, and not all findings are consistent or broadly established.
- Athletes should consider variability in response, possible interactions, and regulatory status before use.
- Safety is generally favorable at standard doses, but long-term or high-dose risks remain poorly characterized.
- Individualized implementation and continuous monitoring are key for those considering Fenugreek supplementation.
Quick Facts Table
| Attribute | Detail |
|---|---|
| Compound Name | Fenugreek |
| Compound Type | Supplements |
| Common Forms | Capsules, powders, teas |
| Primary Uses | Muscle, metabolism, hormone support |
| Human Evidence | Mixed/Context-dependent |
| Typical Dose Range | 500–1,000 mg/day (contextual) |
| Regulatory Status | Legal, varies by country |
| Natural Source | Trigonella foenum-graecum (seed) |
| WADA Status | Not prohibited (as of now) |
| Athlete Population Use | Recreational to elite athletes |
What is Fenugreek?
Fenugreek is a plant-derived supplement sourced from the seeds of Trigonella foenum-graecum, a herb long used in traditional medicine. Recently, it has gained attention in the performance and bodybuilding communities based on its purported effects on muscle strength, body composition, and metabolic processes. Fenugreek is generally consumed in capsule, powder, or tea form, with dosing and composition varying across commercial products.
History & Development
Tongue-tickling in Middle Eastern and South Asian cooking for centuries, Fenugreek’s roots in human use stretch back thousands of years for culinary and medicinal purposes. Its seeds contain unique compounds such as saponins, alkaloids, and fibers believed to be responsible for its physiological effects. Modern research began to examine Fenugreek supplements for their possible role in hormone balance, muscle strength, metabolic control, and recovery, especially in physically active populations.
How Fenugreek Works
Mechanism of Action
Fenugreek’s exact mechanisms in humans have not been fully mapped out, but several consensus-level physiological actions are noted in the existing literature:
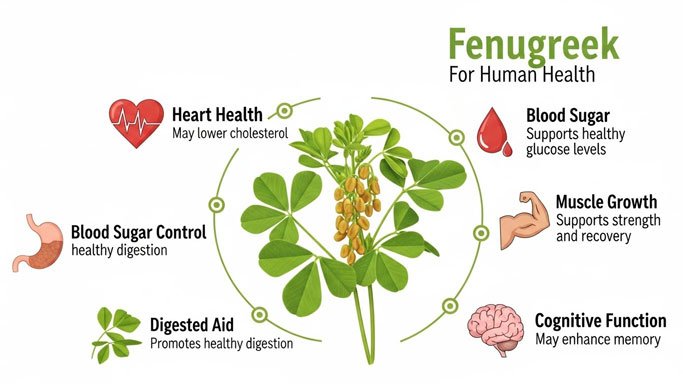
- Hormonal modulation (including effects on testosterone and insulin): Human research suggests Fenugreek may influence hormone metabolism, particularly by modulating enzymes involved in testosterone and glucose regulation. However, consistency and magnitude of these effects in athletes vary widely.
- Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions: Some human trials report reductions in markers of oxidative stress and inflammation, which could theoretically support recovery, but findings are not universal.
- Metabolic impact: Controlled studies in non-athlete and mixed populations indicate Fenugreek may affect glucose uptake, appetite, and lipid metabolism, though direct translation to enhanced athletic performance remains unproven.
Biological Effects
Consensus-level evidence points to several possible biological effects relevant to athletes and bodybuilders:
- Potential increases in free testosterone or support for hormonal balance
- Modest impact on fasting glucose and insulin sensitivity
- Possible reductions in inflammation and oxidative markers
- Alterations in appetite control and satiety signals
- Support for recovery and muscle synthesis (mechanistically plausible; human evidence is mixed)
Individual response may depend on baseline hormonal status, training load, type of Fenugreek supplement (standardized extract vs. seed powder), and overall nutritional context.
Benefits of Fenugreek
1. Hormonal Balance and Testosterone Support
Human research suggests Fenugreek supplementation may influence hormonal status, specifically increasing free testosterone or supporting healthy testosterone levels in some men. This effect appears context-dependent, with some studies noting benefits mainly in individuals with low-normal testosterone or during intensive training. However, not all evidence is positive; variations in extract type, dose, and study population result in inconsistent findings.
2. Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity
Controlled trials indicate Fenugreek can support decreased fasting glucose and improved insulin sensitivity across a range of populations, including some physically active groups. While this metabolic support may theoretically benefit body composition and recovery, evidence in dedicated athlete populations is limited. Effects are generally modest and best interpreted as supportive rather than transformative.
3. Muscle Strength and Body Composition
Evidence regarding Fenugreek for direct improvements in muscular strength or lean mass is mixed. Some trials in resistance-trained individuals report potential benefits when Fenugreek is combined with structured exercise, possibly via indirect hormonal or metabolic pathways. Still, a substantial number of studies have found no significant effects. Variability in supplement composition and training protocols may explain these differences.
4. Recovery and Inflammation
Fenugreek’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties are supported by some human evidence, suggesting a role in attenuating muscle soreness and promoting faster recovery after exercise-induced muscle damage. However, results are inconsistent and often modest. Further research is needed to confirm robust benefit in athletic populations.
5. Appetite Control and Fat Loss
Some human interventions report enhanced satiety or appetite reduction with Fenugreek use, potentially supporting body composition goals when combined with appropriate nutrition and training. Effects are variable and seem more pronounced in individuals with higher body fat or during energy restriction phases.
6. Lipid Profile Modulation
Human research indicates possible improvements in cholesterol and lipid markers with Fenugreek supplementation, although translation to athletic performance or health for already fit populations remains uncertain.

Side Effects & Safety
1. Digestive Discomfort
The most commonly reported side effects of Fenugreek supplementation include digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and mild gastrointestinal discomfort. These effects are generally mild and dose-dependent.
2. Allergic Reactions
Fenugreek is a legume and may provoke allergic responses in sensitive individuals, particularly those allergic to peanuts or chickpeas. Symptoms can range from mild (rash, itching) to severe (anaphylaxis), though such reactions are rare.
Interactions
- Drug interactions: Fenugreek may interact with antidiabetic, anticoagulant, or antiplatelet medications. There is also a theoretical risk of additive effects with other herbal supplements impacting blood sugar or clotting.
- Monitoring: Individuals using prescription medications should consult with a healthcare provider before starting Fenugreek supplements.

Additional considerations:
- Long-term safety: Human safety data for prolonged, high-dose use in athletes is limited.
- Contraindications: Pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those with hormone-sensitive conditions, should avoid Fenugreek unless medically advised.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Potential support for hormone balance | Digestive discomfort risk |
| May aid glucose management | Allergic reactions (rare) |
| Possible anti-inflammatory effects | Evidence in athletes inconsistent |
| Widely available, legal | Drug/supplement interactions possible |
| Natural plant source | Long-term/high-dose safety unknown |
| Easy to administer | Not a replacement for evidence-based therapies |
How Athletes & Bodybuilders Use Fenugreek
Practical Usage Scenarios
- Body recomposition phases: Employed during fat loss phases to support appetite control and hormonal balance.
- Intensive training blocks: Considered by some athletes seeking to support recovery, muscle synthesis, or maintain anabolic environment during high training loads.
- Blood sugar regulation: Used by those aiming to optimize glucose control, particularly if combining high-volume training with dietary carbohydrate manipulation.
Timing, Forms, & Implementation
- Standardized extract vs. whole seed: Most human trials focus on extracts standardized for saponin or protodioscin content.
- Typical timing: Usually taken with meals to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort and leverage possible effects on postprandial metabolism.
- Capsule, powder, or tea: Athletes typically prefer capsules for convenience and consistency of dosing.
- Cycle length: Evidence is insufficient to recommend specific cycling strategies; most protocols mirror research durations of 4–12 weeks.
Monitoring & Safety Notes
- Track subjective effects and performance metrics.
- Monitor for gastrointestinal or allergic symptoms—discontinue if reactions occur.
- Regularly review medication interactions with a healthcare professional.
- Avoid stacking with unproven or similar-effect supplements without clear rationale.
Comparison to Similar Compounds
Overview:
| Feature | Fenugreek | Tribulus Terrestris | DHEA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supports testosterone | Possible in some cases | Unproven/mixed | Direct precursor |
| Impacts glucose metabolism | Yes | Not established | Weak evidence |
| Legal status | Generally legal | Generally legal | Prescription-only in some countries |
| Side effect profile | Digestive, allergic | Rare, mild | Hormonal, metabolic |
| Strength of evidence | Moderate, context-specific | Weak | Limited in athletes |
Analysis
Fenugreek is often compared to other herbal and hormonal supplements for similar purposes. Unlike Tribulus terrestris, Fenugreek has limited but clearer evidence for metabolic and hormonal effects. Compared to DHEA, Fenugreek’s mechanisms are indirect, and its legal status is less restrictive. However, neither is a substitute for clinically indicated therapies or proven performance-enhancing drugs.
Legality & Regulatory Status
Fenugreek is legally available as a dietary supplement in most countries. It is not classified as an anabolic steroid, nor is it currently listed by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) as a prohibited substance. Nevertheless, contamination or mislabeling risks exist in the supplement market—athletes should source products from reputable suppliers and remain updated on regulatory changes.
Where to buy “Fenugreek”?

Fenugreek supplements are widely sold in natural health stores, supplement retailers, and online platforms. When purchasing, athletes should prioritize third-party-tested products, ideally standardized for active compounds, and avoid proprietary blends or unverified purity. Price, formulation, and extract quality vary widely—review ingredient labels and select forms matching those used in clinical research when possible.
Alternatives to Fenugreek
Several supplements share similar use cases or mechanisms:
- Ashwagandha: Adaptogen with some evidence for stress resilience and testosterone support.
- Creatine: Well-established for muscle and performance enhancement, not hormonal impact.
- DHEA or other prohormones: Direct hormonal precursors, but legal and safety issues are more pronounced.
- Dietary modifications: Protein timing and macronutrient manipulation often have a greater impact than single-ingredient supplementation.
- Lifestyle factors: Sleep, stress management, and adequate recovery are foundational and outperform most herbal strategies for athletes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is Fenugreek a proven testosterone booster for athletes?
Evidence is mixed—some human trials suggest benefits in certain populations, but effects are not reliable or universal.
Can it enhance strength or muscle mass?
Results are inconsistent; some studies in resistance-trained individuals suggest potential support, while others find no benefit.
How should athletes dose Fenugreek?
Typical regimens use 500–1,000 mg of standardized extract daily, split with meals. Individual needs and tolerances vary.
What are the main side effects?
Digestive discomfort and rare allergic reactions. Long-term safety is unclear, especially with high doses or stacking.
Is it legal for competition?
As of now, yes—it is not prohibited by most sporting bodies, but contamination or mislabeling remains a concern.
Can women athletes use it?
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not recommended. Effects on female hormones are incompletely understood.
Conclusion
Fenugreek is a versatile herbal supplement offering possible support for hormone modulation, glucose metabolism, and recovery processes relevant to some athletes and bodybuilders. Human research provides modest, context-dependent evidence—with effects most notable for metabolic support and hormonal balance in specific populations.
Variability in individual response, uncertainty about long-term safety, and the need for careful monitoring highlight the importance of a cautious, personalized approach. Fenugreek should complement, not replace, evidence-based nutrition and training strategies, and athletes should prioritize transparency, quality, and medical oversight in all supplementation decisions.
Athlete Final Checklist
Focus on foundational nutrition, training, and recovery as primary performance drivers.
Assess need: Confirm specific goal (hormone support, glucose metabolism, recovery).
Check legal and regulatory status in your sport and country.
Source high-quality, third-party-tested Fenugreek supplements.
Start with a low dose and monitor for side effects.
Track subjective and objective performance metrics.
Review all medications and supplements for interactions.
Re-evaluate use periodically; discontinue if adverse effects occur or if benefits are not measurable.